Analytics¶
Adobe Analytics¶
If your organization already subscribes to Adobe Analytics, rich PDF analytics is yours by default. You should use Analytics as you normally would; however, there are a few setup steps required to correctly map the incoming data to Adobe Analytics variables.
Set up the PDF Viewer¶
Since you want to track user interaction with the PDF viewer, you need to make sure events appear in the correct report suites. To automatically receive PDF analytics events, pass the Analytics report suite ID when creating the AdobeDC.View instance. You must ensure that Adobe Analytics is instrumented using the same reportSuiteId for the website where you are embedding the PDF Viewer.
var adobeDCView = new AdobeDC.View({
clientId: "<YOUR_CLIENT_ID>",
divId: "adobe-dc-view"
reportSuiteId: <YOUR_Adobe_Analytics_REPORT_SUITE ID>,
...
})
Configure Adobe Analytics¶
The current release requires a few configuration steps to correctly map PDF Embed API data collected from your PDF viewer to your report suite. Once you’ve logged in to Analytics, do the following:
Once you’ve logged in to Analytics, do the following:
In the top menu, go to Admin > Report Suites.
Select your report suite.
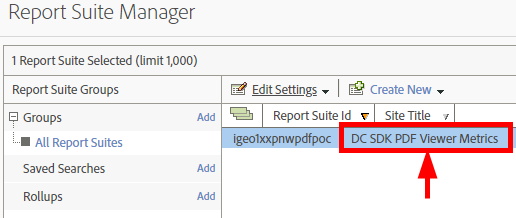
Navigate to the Report Suite Manager.
Highlight your report suite.
Choose Edit Settings > General > Processing Rules.
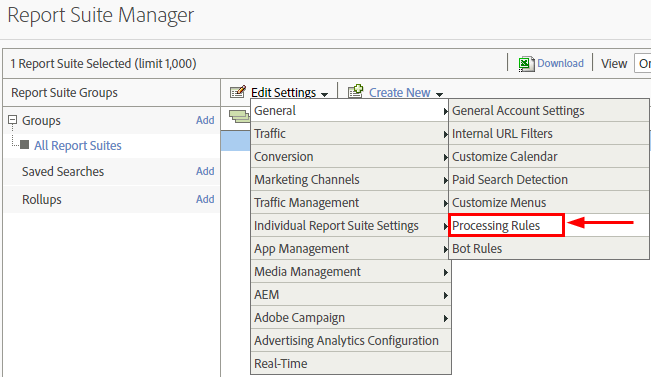
Click the Processing Rules tab. You’ll need to create two rules and configure them so that you can map collected events and event attributes to Analytics variables.
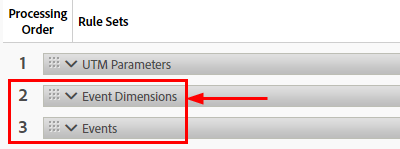
Mapping event attibutes¶
You’ll need to create a new rule and map event attributes sent by the PDF Embed API to an Adobe Analytics variable. For example, an event attribute might be something like a page number or title. There could be many events with the same attribute (one for each event happening on a specific page). The following attributes eventually become dimensions in your reports:
a.dc.searchTerm
a.action
a.dc.pageNum
a.dc.filename
Map event attributes as follows:
Choose Add Rule.
Add a custom rule title such as “Event Dimensions”.
Choose Add Action until you have four (one for each attribute above).
Select an item (event attribute) from the With drop down list (one of those above).
Select an Analytics dimension variable from the drop down list on the left.
The left hand columns should remain set to “Overwrite value of”.
Repeat the above steps for each incoming event attribute you track.
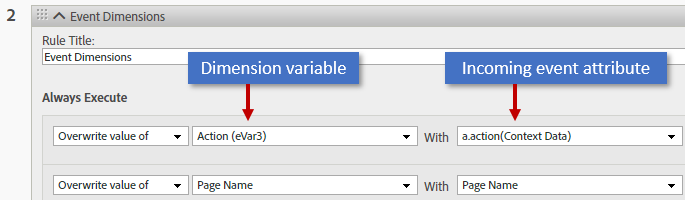
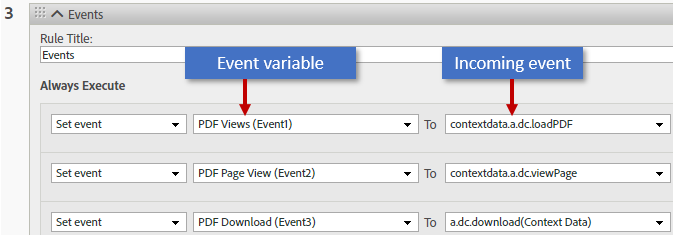
Mapping events¶
Create another new rule and map events sent by the PDF Embed API to an Adobe Analytics variable. Note that Analytics uses “metrics” and “events” interchangeably. An event is any user interaction your JavaScript event listener captures; for example, clicking on a button or commenting on a PDF. The following events eventually become metrics displayed in your reports:
a.dc.zoomLevel
a.dc.loadPDF
a.dc.viewPage
a.dc.download
a.dc.search
a.dc.bookmarkClicked
a.dc.copyText
a.dc.print
Map events as follows:
Choose Add Rule.
Add a custom rule title such as “Events”.
Choose Add Action until you have eight (one for each attribute above).
Select a metric (an event) from the To drop down list (one of those above).
Select an Analytics event variable from the drop down list on the left.
The left hand column should remain set to “Set event”.
Repeat the above steps for each metric (incoming event).
Viewing your data¶
Set up your reporting as usual, and view the dimensions and metrics in your workspace.
Help, support, forum¶
For more detail about using this Adobe Analytics UI, refer to the help docs. You can also ask questions and get help here:
Default analytics¶
If you are not subscribed to Adobe Analytics, you can still collect PDF analytics events as users interact with PDFs. You enable PDF analytics events by registering a callback with the API to listen the events. Tracking PDF events provides insight into user actions and thereby helps you manage and evolve the PDF experience you’re delivering to customers.
As always, initialize the AdobeDC View object with your client ID, and then invoke the previewFile API on AdobeDC.View object as usual. Finally, register the callback to receive the events and set enablePDFAnalytics to true:
1 const eventOptions = {
2 //Pass the PDF analytics events to receive.
3 //If no event is passed in listenOn, then all PDF analytics events will be received.
4 listenOn: [ AdobeDC.View.Enum.PDFAnalyticsEvents.PAGE_VIEW, AdobeDC.View.Enum.PDFAnalyticsEvents.DOCUMENT_DOWNLOAD],
5 enablePDFAnalytics: true
6 }
7
8 adobeDCView.registerCallback(
9 AdobeDC.View.Enum.CallbackType.EVENT_LISTENER,
10 function(event) {
11 console.log("Type " + event.type);
12 console.log("Data " + event.data);
13 }, eventOptions
14 );
Find the working example in the samples repo under /More Samples/Capture PDF Embed API Events/.
Event type |
Event description |
Event data |
|---|---|---|
DOCUMENT_OPEN |
On successful opening of PDF. |
{fileName: <FILE_NAME>} |
PAGE_VIEW |
Page information on change in page(s) in view |
{pageNumber: <PAGE_NUM>, fileName: <FILE_NAME>} |
BOOKMARK_ITEM_CLICK |
On clicking on any bookmark item |
{title: <BOOKMARK_TITLE>, fileName: <FILE_NAME>} |
DOCUMENT_DOWNLOAD |
When the PDF is downloaded |
{fileName: <FILE_NAME>} |
DOCUMENT_PRINT |
When the PDF is printed |
{printSupported: true, fileName: <FILE_NAME>} |
HYPERLINK_OPEN |
On clicking any external hyperlink in the PDF |
{type: “external”, pageNumber: <PAGE_NUM>, x: <X-coordinate of the link>, y: <Y-coordinate of the link>, url: <EXTERNAL_URL>} |
TEXT_COPY |
On copying any text from a PDF. Note that the TEXT_COPY event only fires for PDF files that allow text copy; for example, secured and encrypted files do not allow copying text. |
{copiedText: <COPIED_TEXT>, fileName: <FILE_NAME>} |
TEXT_SEARCH |
When the user searches for any text via the document search field |
{searchedText: <SEARCHED_TEXT>, fileName: <FILE_NAME>} |
ZOOM_LEVEL |
When zoom in/out actions are performed from the page control toolbar |
{zoomLevel: <ZOOM_LEVEL>, fileName: <FILE_NAME>} |
Basic events¶
In addition to the PDF analytics events, the PDF Embed API supports events which provide insight into user actions taken related to file preview. These events can be received through the events callback. After registering the events callback, the following file preview events are generated:-
Event type |
Event description |
Event data |
|---|---|---|
APP_RENDERING_START |
When the PDF starts to render in the viewer. |
None |
APP_RENDERING_DONE |
When the first page of the PDF is displayed in the viewer.. |
None |
APP_RENDERING_FAILED |
When the PDF fails to render because of an unexpected error. |
None |
PDF_VIEWER_OPEN |
When the PDF viewer opens. |
None |
PDF_VIEWER_CLOSE |
When the PDF viewer closes. |
None |
PDF_VIEWER_READY |
When the PDF is rendered completely and the PDF viewer is ready to perform functionalities, such as, annotations and form-filling. This event is especially useful in case of linearized PDFs to check when the PDF gets fully downloaded. To know more about linearization, see the section PDF Linearization. |
None |
In order to receive additional file preview events, set enableFilePreviewEvents to true and pass it to the events callback. To receive specific events, pass the list of event types in the listenOn parameter. If nothing is passed to listenOn, then the API returns all the file preview events.
1 const eventOptions = {
2 //Pass the events to receive.
3 //If no event is passed in listenOn, then all file preview events will be received.
4 listenOn: [ AdobeDC.View.Enum.Events.APP_RENDERING_START, AdobeDC.View.Enum.FilePreviewEvents.PREVIEW_KEY_DOWN, AdobeDC.View.Enum.FilePreviewEvents.PREVIEW_PAGE_VIEW_SCROLLED ],
5 enableFilePreviewEvents: true
6 }
7
8 adobeDCView.registerCallback(
9 AdobeDC.View.Enum.CallbackType.EVENT_LISTENER,
10 function(event) {
11 console.log(event)
12 }, eventOptions
13 );
Event type |
Event description |
Event data |
|---|---|---|
PREVIEW_KEY_DOWN |
Any keyboard key is pressed over any PDF page. |
{ altKey: <BOOLEAN>, code: <KEY_VALUE>, composed: <BOOLEAN>, ctrlKey: <BOOLEAN>, key: <KEYBOARD_CHARACTER>, keyCode: <KEY_CODE>, location: <LOCATION>, metaKey: <BOOLEAN>, shiftKey: <BOOLEAN>, type: “keydown” } |
PREVIEW_PAGE_VIEW_SCROLLED |
The PDF page is scrolled. |
{ clientHeight: <CLIENT_HEIGHT>, clientWidth: <CLIENT_WIDTH>, scrollHeight: <SCROLL_HEIGHT>, scrollWidth: <SCROLL_WIDTH>, scrollLeft: <SCROLL_LEFT>, scrollTop: <SCROLL_TOP> } |
PREVIEW_DOCUMENT_CLICK |
A user clicks on the area in the webpage which is outside the PDF preview (excluding the top bar and left hand panel). |
{ clientX: <CLIENT_WIDTH>, clientY: <CLIENT_HEIGHT>, pageX: <PAGE_WIDTH>, pageY: <PAGE_HEIGHT>, screenX: <SCREEN_WIDTH>, screenY: <SCREEN_HEIGHT> } |
PREVIEW_PAGE_CLICK |
A user clicks on any PDF page. |
{ pageNumber: <PAGE_NUMBER> } |
PREVIEW_PAGE_DOUBLE_CLICK |
A user double-clicks on any PDF page. |
{ pageNumber: <PAGE_NUMBER> } |
PREVIEW_PAGE_MOUSE_ENTER |
The mouse pointer enters any PDF page. |
{ pageNumber: <PAGE_NUMBER> } |
PREVIEW_PAGE_MOUSE_LEAVE |
The mouse pointer leaves any PDF page. |
{ pageNumber: <PAGE_NUMBER> } |
CURRENT_ACTIVE_PAGE |
Returns the page number of the current page in view. |
{ pageNumber: <PAGE_NUMBER> } |
PREVIEW_SELECTION_END |
Any text is selected in the PDF. |
{ startPageNumber: <PAGE_NUMBER>, endPageNumber: <PAGE_NUMBER>, newSelection: <BOOLEAN>, selections: { page<PAGE_NUMBER>: { bbox0: { deviceBottom: <Ymin-coordinate>, deviceLeft: <Xmin-coordinate>, deviceRight: <Xmax-coordinate>, deviceTop: <Ymax-coordinate> }, bbox1: {…}, bbox2: {…}, …, bboxCount: <BBOX_COUNT> }} } |
PREVIEW_ZOOM |
A zoom operation is applied to any PDF page. |
<ZOOM_LEVEL> |
PAGES_IN_VIEW_CHANGE |
The page in view changes to a different page through scrolling or page navigation. |
{ startPage: { pageNumber: <PAGE_NUMBER>, fractionVisible <PAGE_VISIBLE_FRACTION> }, endPage: { pageNumber: <PAGE_NUMBER>, fractionVisible <PAGE_VISIBLE_FRACTION> }} |
UNSUPPORTED_FEATURE_FOUND |
When user tries to use an unsupported feature in PDF Embed API. The event data provides information about the type of unsupported feature in the featureName field and relevant metadata of PDF in the data field. For example, XFA form fields are not supported in PDF Embed API and this event is generated when a user tries to fill any such form field. |
{ featureName: <FEATURE_NAME>, data: {hasJS: <BOOLEAN>, hasUnsupportedActions: <BOOLEAN, hasUnsupportedWidget: <BOOLEAN>, hasXFA: <BOOLEAN> }} |
Annotation events¶
Web developers can receive events when a user interacts with an annotation. These events are generated for annotation actions performed through the UI.
To register the events callback, set enableAnnotationEvents to true and pass it to the callback. To receive specific events, pass the list of annotation event types in the listenOn parameter. If nothing is passed to listenOn, then the API returns all the annotation events.
1const eventOptions = {
2 //Pass the events to receive.
3 //If no event is passed in listenOn, then all annotation events will be received.
4 listenOn: [ AdobeDC.View.Enum.AnnotationEvents.ANNOTATION_ADDED, AdobeDC.View.Enum.AnnotationEvents.ANNOTATION_UPDATED ],
5 enableAnnotationEvents: true
6 }
7
8 adobeDCView.registerCallback(
9 AdobeDC.View.Enum.CallbackType.EVENT_LISTENER,
10 function(event) {
11 console.log(event.type, event.data)
12 }, eventOptions
13 );
Event type |
Event description |
Event data |
|---|---|---|
ANNOTATION_ADDED |
A new annotation is added to PDF. |
<ANNOTATION_TYPE> |
ANNOTATION_CLICKED |
An existing annotation is clicked. |
<ANNOTATION_TYPE> |
ANNOTATION_UPDATED |
An existing annotation is updated. |
<ANNOTATION_TYPE> |
ANNOTATION_DELETED |
An annotation is deleted. |
<ANNOTATION_TYPE> |
ANNOTATION_MOUSE_OVER |
The cursor moves over any annotation. |
<ANNOTATION_TYPE> |
ANNOTATION_MOUSE_OUT |
The cursor moves out of any annotation. |
<ANNOTATION_TYPE> |
ANNOTATION_SELECTED |
Any existing annotation is selected. |
<ANNOTATION_TYPE> |
ANNOTATION_UNSELECTED |
A selected annotation is unselected |
<ANNOTATION_TYPE> |
ANNOTATION_MODE_STARTED |
The user selects a particular annotation type from the toolbar. |
<ANNOTATION_TYPE> |
ANNOTATION_MODE_ENDED |
A user exits any previously selected annotation mode. |
<ANNOTATION_TYPE> |
ANNOTATION_COUNT |
Denotes the total number of annotations when any new annotation is added or any existing annotation is deleted. |
<NUMBER_OF_ANNOTATIONS> |
Note
If annotation APIs are not enabled, the event data contains the type of annotation on which the event gets triggered.
If annotation APIs are enabled, the event data contains the data of the annotation in JSON format on which the event gets triggered.